* cess à接二連三的
Examples: successive, process
* successive
Definition:
adjective
1.following in order or in uninterrupted sequence; consecutive: three successive days.
2.following another in a regular sequence: the second successive day.
3.characterized by or involving succession.
Origin:
1400–50; late Middle English < Medieval Latin successīvus, equivalent to success ( us ), past participle ofsuccēdere to succeed + -īvus -ive
Examples:
1.Earnings set a new record for the seventhsuccessive year.
2. Successive reappointments of up to four yearseach are possible.
* process
Definition:
1.a systematic series of actions directed to some end: to devise a process for homogenizing milk.
2.a continuous action, operation, or series of changes taking place in a definite manner: the process ofdecay.
Origin:
1275–1325; Middle English proces (noun) (< Old French ) < Latin prōcessus a going forward, equivalent toprō- pro-1 + ced-, variant stem of cēdere to yield (see cede) + -tus suffix of v. action; see cession
Examples:
As you can see, the process is not easilypredictable, and it is subject to the influence ofthe personalities of those involved.
* dià一分為二
Examples: divorce, divide, distroy
* wiretap
Definition:
noun
1.an act or instance of tapping telephone or telegraph wires for evidence or other information.
verb (used with object)
2.to obtain (information, evidence, etc.) by tapping telephone or telegraph wires: to wiretapconversations.
3.to listen in on by means of a wiretap: to wiretap a telephone; to wiretap a conversation.
verb (used without object)
4.to tap telephone or telegraph wires for evidence, information, etc.
adjective
5.pertaining to or obtained by wiretap.
Origin:
1950–55; back formation from wiretapper
Examples:
It is also immaterial where the physicalconnection of the wiretap takes place.
Courts unlikely to hear wiretap cases, legalscholars say.
* ratification
Definition:
noun
1.the act of ratifying; confirmation; sanction.
2.he state of being ratified.
Origin:
1400–50; late Middle English < Medieval Latin ratificātiōn- (stem of ratificātiō ), equivalent to ratificāt ( us )(past participle of ratificāre to ratify) + -iōn- -ion
Examples:
1. fact, both ratification and reciprocity are redherrings.
2.rst, the political timetable for its ratification could slip.
* The Age of Innocence 純真年代

Tale of 19th century New York high society in which a young lawyer falls in love with a woman separated from her husband, while he is engaged to the woman's cousin.
* Rip Van Winkle

"Rip Van Winkle" is a short story by American author Washington Irving published in 1819 as well as the name of the story's fictional protagonist. Written while Irving was living in Birmingham, England, it was part of a collection entitled The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent.. Although the story is set in New York's Catskill Mountains, Irving later admitted, "When I wrote the story, I had never been on the Catskills."
* American literature can be divided into three major periods including colonial literature, the revolutionary period and the romantic period.
1607 - 1775: Colonial Period
William Bradford
John Winthrop
Cotton Mather
Benjamin Franklin
Anne Bradstreet
1765 - 1790: Revolutionary Age
Thomas Jefferson
Alexander Hamilton
James Madison
Thomas Paine
1775 - 1865: Early National Period
James Fenimore Cooper
Edgar Allan Poe
William Cullen Bryant
Frederick Douglass
Harriet Jacobs
(slave narratives)
1828 - 1865: Romantic Period in America (American Renaissance or Age of Transcendentalism)
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Henry David Thoreau
Edgar Allan Poe
Herman Mellville
Washington Irving
Nathaniel Hawthorne
Harriet Beecher Stowe
John Greenleaf Whittier
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Walt Witman
* Benjamin Franklin

Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706 [O.S. January 6, 1705][Note 1][Note 2] – April 17, 1790) was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his discoveries and theories regarding electricity. He invented the lightning rod, bifocals, the Franklin stove, a carriage odometer, and the glass 'armonica'.[1] He facilitated many civic organizations, including a fire department and a university.
Quotes:
1.Time is money.
2.No pain, no gain
* Promised Land
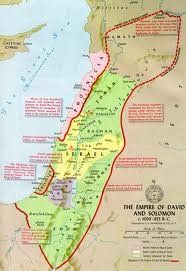
The Promised Land is the land promised or given by God, according to theTanakh (the Hebrew Bible), to the Israelites, the descendants of Jacob. The promise is first made to Abraham (Genesis 15:18-21) and then renewed to his son Isaac, and to Isaac's son Jacob (Genesis 28:13), Abraham's grandson. The promised land was described in terms of the territory from the River of Egypt to the Euphrates river (Exodus 23:31) and was given to their descendants after Moses ledthe Exodus out of Egypt. (Deuteronomy 1:8)
* Partisan feeling must yield to patriotism.
* Hillary Cliton – Action is Eloquence
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dvUfEpaPOls

American Dream and Carly Simon's "Let the River Run" from movie Working Girl
* Thomas Jefferson – Empire of Liberty

The Empire of Liberty is a theme developed first by Thomas Jefferson to identify America's world responsibility to spread freedom across the globe. Jefferson saw America's mission in terms of setting an example, expansion into the west, and by intervention abroad. Major exponents of the theme have been Abraham Lincoln (in the Gettysburg Address), Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilson (and "Wilsonianism"), Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry Truman, Ronald Reagan, Bill Clinton,[1] and George W. Bush.


 留言列表
留言列表

